The long head of the biceps tendon runs in a groove at the front of the shoulder (the bicipital groove). The tendon can become inflamed and damaged either through overuse (weightlifting and overhead sports) or simply with time
The patient usually complains of a pain in the front of the shoulder. The tendon is usually tender to touch adn the pain is made worse with overhead activities and exercises which load the biceps muscle.
How is the diagnosis made?
The clinician will take a full history and examine the shoulder and arm. Ultrasound can often reveal fluid around the tendon and damage within the tendon. MRI can is occasionally used and can help to rule out other problems inside the joint.
Investigations include:
- Xray
- MRI
- Ultrasound
What is the initial treatment?
The initial treatment is symptomatic and includes rest and anti-inflammatories. An injection around the tendon in the groove may be suggested. This does not always solve the problem but can be useful in confirming the diagnosis.
Physiotherapy can be beneficial at this stage.
If initial treatment doesn’t work, what’s next?
The patients may complain of a persistent ache in the front of the arm, made worse by lifting or carrying.
If the symptoms are intrusive enough then biceps tenodesis may be necessary.
Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis
Anaesthetic
General Anaesthetic with an interscalene block (Fully asleep with a local anaesthetic injection into the side of the neck will numb the nerves to the shoulder for post-operative pain relief)
More information about nerve blocks can be found here
Operation type
Arthroscopic (keyhole) and open (small incision)
Incisions
2 ½ cm incisions will be made in the shoulder, one to the back and at the front of the shoulder as well a 5cm incision just under the armpit.
Procedure
The gleno-humeral (shoulder) joint will be inspected first. The damaged biceps is cut inside the joint
The muscles and tendons of the upper arm are moved to each side and the end of the long head of biceps tendon is identified. The muscle is freed as much as possible but it is usually not possible to restore it to its pre-injury position. A small hole is drilled in the front of the humerus and the tendon stump is secured to the bone using a kevlar stitch.
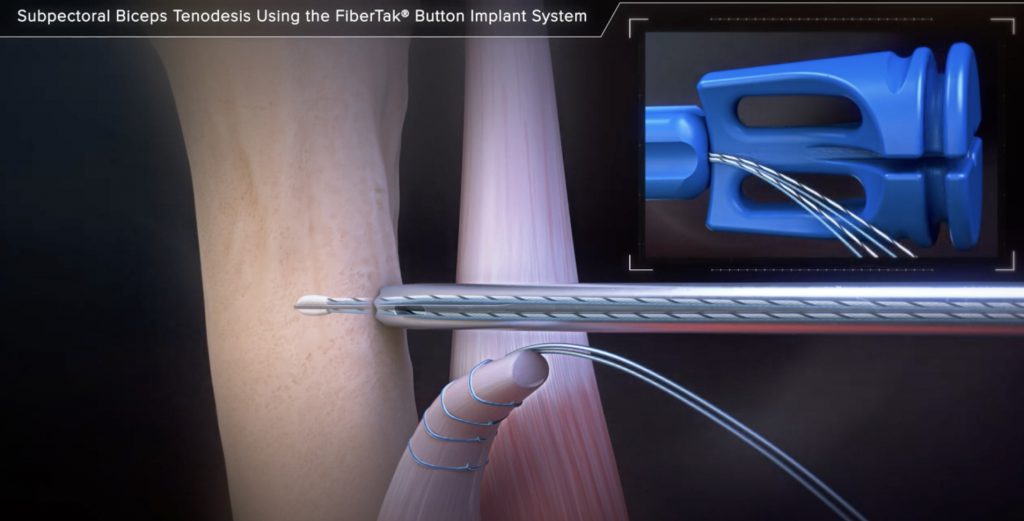
Biceps tenodesis 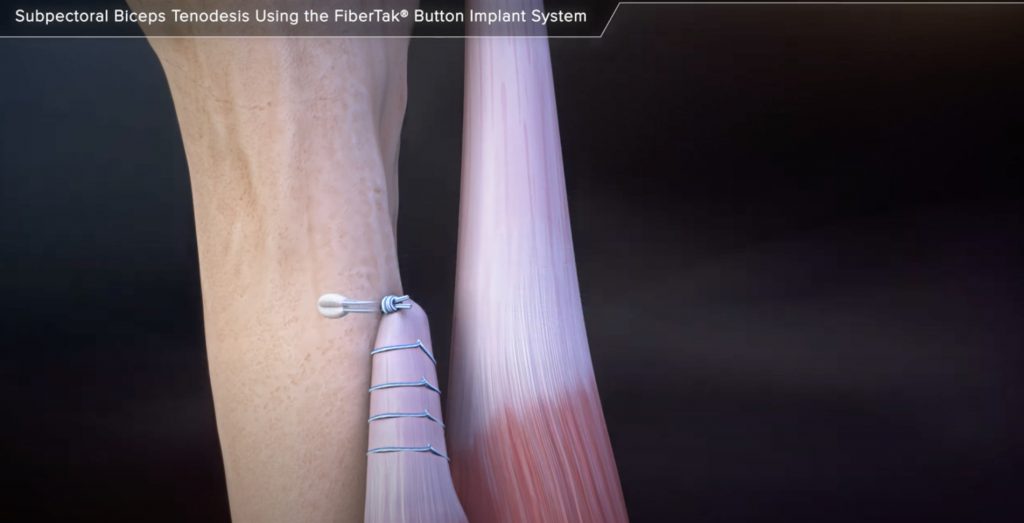
Completed repair
A video of the procedure can be found here
Wound Closure
Small butterfly paper stitches will be used to close the wounds.
Tegaderm waterproof dressings will be placed over the top of the paper stitches.
Pain relief
The anaesthetist will discuss a nerve block which will be administered after you are asleep, this means that you will wake up with no pain in the shoulder but the arm will feel numb for up to 12 hours. You will be prescribed painkillers to start taking when you get home and we encourage you to take these regularly for at least the first few days. There will be some discomfort but this settles quite rapidly and ice packs can be used in addition if you wish.
Wound care
The dressings will be changed before you go home and these can be left alone until they are removed. Typically they can be removed 10 days after surgery just by peeling them off and you do not need to visit the doctor for this.
The dressings are showerproof and you will be given some spares in case they start to peel off.
Rehabilitation after surgery
You will wake up with a sling on your arm. This is worn for comfort and to remind you to be careful with the arm.

- Wound care: The dressings are showerproof and you can leave them on for 10 days after which they can simply be peeled off.
- Keep moving your hand to keep your wrist from becoming stiff
Phase 2: 3-6 weeks
- You will be seen in the clinic at 3 weeks
- If you are not already doing so start working on forward elevation (lift the arm to the front to the horizontal)
- Aim: Forward and side elevation to horizontal by 6 weeks
Phase 3: 6-12 weeks
- Physiotherapy should start at this stage
- Start working on range of motion exercises
- Start rotator cuff strengthening exercises
Surgical Risks
Every operation has an degree of risk. It is important that you are aware of these risks before you agree to proceed with your operation.
If you decide not to proceed with surgery there is a possibility that the symptoms will settle on their own but they may continue and they may get worse. You will not damage the shoulder if you decide not to proceed with surgery.
The most common or significant risks are outlined below. A risk of 0.1% means that 1 in 1000 people will suffer the complication
- Failure of the procedure to relieve symptoms: 5%
- Superficial Infection (requiring antibiotics): 0.16%
- Deep Infection (requiring further surgery): 0.02%
- PE (Pulmonary Embolus) (Blood clot in the lung): 0.13% – Blood thinning medication is required for several months. Can rarely result in death.
- DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) (Blood clot in the leg): 0.14% – Blood thinning medication is required for several months. Can lead to PE
- Nerve Injury: 0.01% – Usually temporary. Can cause weakness around the shoulder with loss of function and rarely can be permanent.
- Heart attack: 0.02%
- To put these numbers in perspective
The chance of:- Getting three balls in the UK national lottery: 0.9%
- Needing emergency treatment in the next year after being injured by a can, bottle, or jar: 0.1%
- Death by an accident at home: 0.01%
- For a 50 year old man in good health the 5 year risk of dying is 0.8%
Frequently asked questions
Return to work after surgery
This is very much dependent on the type of work that you do, whether you need to drive to get to work and the type of surgery that you have had done.
You, as the patient, have the best idea of the specific demands that are required of you to do your work safely and effectively.
Having an operation with an anaesthetic often takes more out of people than they would expect. Generally it is probably worth taking at least a week off from your regular work after having had any procedure.
You should discuss expected post-operative recovery and work with the surgeon before your operation.
Driving after surgery
To be able to drive safely you should be capable of actively moving your shoulder without assistance and without damaging the surgical repair. You should be able to react normally to avoid causing injury to yourself or others due to a lack of control.
Typically this is a MINIMUM eight weeks after a shoulder stabilisation.
It is a UK requirement that, unless specific dispensation has been granted by the DVLA, a driver uses both arms to control the steering wheel.
It is the responsibility of the driver to ensure that they are in control of the vehicle at all times. They should be able to demonstrate this if stopped by the police.
It is not a requirement to notify the DVLA unless the medical conditions likely to affect safe driving persist for longer than three months after the date of the surgery.
Drivers must not drive under the influence of narcotic medications or within a minimum of 24 hours after an anaesthetic.
You are not allowed to drive one-handed and therefore cannot drive whilst you are in the sling.
There is no precise time after surgery when you can return to driving, it varies from person to person. However, the recommended amount of time that your arm should be in a sling following surgery is the MINIMUM time before considering a return to driving.
You can return to driving when you are capable of moving your shoulder without assistance and are capable of driving safely and reacting appropriately in an emergency situation.
Although it is not essential, it may be wise to discuss your return to driving with your car insurance company.
Sports after surgery
You can start simple cardio such as walking or using a static bicycle immediately following surgery as long as you are wearing your sling. Exercises which involve the shoulder cannot start until you have regained reasonable range. This is typically about eight weeks following surgery.
Contact sports and sports in which you are likely to fall over should not be started until you have achieved the full range of motion and your strength is normal and in addition you need to have the confidence in the shoulder that you can fall onto it with no consequences. This can take up to 6 months and you should factor this into your decision to have surgery.